en
-
Products
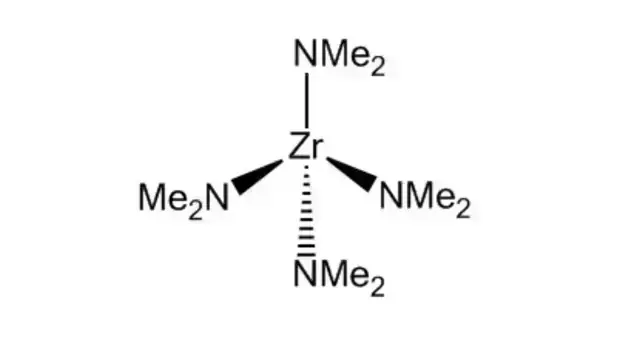
Oxide PowderHafnium Oxide Powder (HfO2) Zirconium Oxide Powder (ZrO2) Yttrium Oxide Powder (Y₂O₃) Lanthanum Oxide Powder (La₂O₃) Cerium Oxide Powder (CeO₂) Praseodymium Oxide Powder (Pr₆O₁₁) Neodymium Oxide Powder (Nd₂O₃) Samarium Oxide Powder (Sm₂O₃) Europium Oxide Powder (Eu₂O₃) Gadolinium Oxide Powder (Gd₂O₃)Carbide PowderTitanium Carbide Powder (TiC) Molybdenum Carbide Powder (Mo2C) Hafnium Carbide Powder (HfC) Zirconium Carbide Powder (ZrC) Vanadium Carbide Powder (VC) Chromium Carbide Powder (Cr3C2) Tungsten Carbide Powder (WC) Niobium Carbide Powder (NbC) Titanium Carbide Powder (TiC) Tantalum Carbide Powder (TaC)Boride PowderNickel Boride Powder (Ni2B) Titanium Diboride Powder (TiB2) Hafnium Diboride Powder (HfB2) Zirconium Diboride Powder (ZrB2) Molybdenum Borohydride Powder (MoB2) Silicon Hexaboride Powder (SiB6) Lanthanum Hexaborate Powder (LaB6) Cerium Hexaborate Powder (CeB6) Vanadium Diboride Powder (VB2) Chromium Diboride Powder (CrB2)Rare Earth Sputtering TargetHigh Purity Lanthanum Sputtering Target (La) High Purity Cerium Sputtering Target (Ce) High Purity Praseodymium Sputtering Target (Pr) High Purity Neodymium Sputtering Target (Nd) High Purity Samarium Sputtering Target (Sm) High Purity Europium Sputtering Target (Eu) High Purity Gadolinium Sputtering Target (Gd) High Purity Terbium Sputtering Target (Tb) High Purity Dysprosium Sputtering Target (Dy) High Purity Holmium Sputtering Target (Ho)Rare Earth Alloy Sputtering TargetMolybdenum Lanthanum Alloy Sputtering Target (MoLa) Aluminum Scandium Alloy Sputtering Target (AlSc) Ytterbium Antimonide Cobalt Alloy Sputtering Target (YbCoSb) Cerium Gadolinium Alloy Sputtering Target (CeGd) Cerium Magnesium Nickel Alloy Sputtering Target (CeMgNi) Samarium Cobalt Alloy Sputtering Target (Sm1Co5) Lanthanum Yttrium Alloy Sputtering Target (LaY) Lanthanum Nickel Alloy Sputtering Target (LaNi) Terbium Dysprosium Iron Alloy Sputtering Target (Tb0.3Dy0.7Fe1.9) Terbium Iron Alloy Target (TbFe) (45/55 at%)
- Applications
- Cas No
- Company
- COA
- Resources
- Contact
 English
English